Automotive Cooling System: Principles, Material Selection, and Maintenance Guide
The cooling system plays a crucial role in managing engine temperature, preventing overheating, and ensuring efficient, stable engine performance. This system works by circulating coolant, absorbing the engine’s heat, and releasing it into the external environment, maintaining the engine at an optimal temperature. This guide delves into the working principles of the cooling system, the pros and cons of different radiator materials, common issues, and essential maintenance tips.
How the Cooling System Works
The cooling system consists mainly of the radiator, thermostat, water pump, fan, and connecting hoses. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:

-
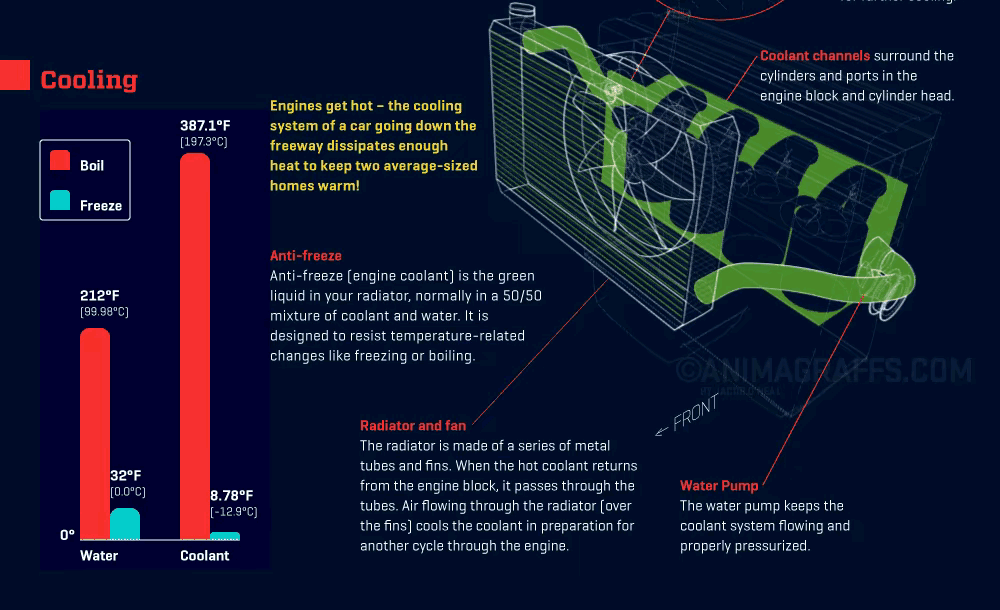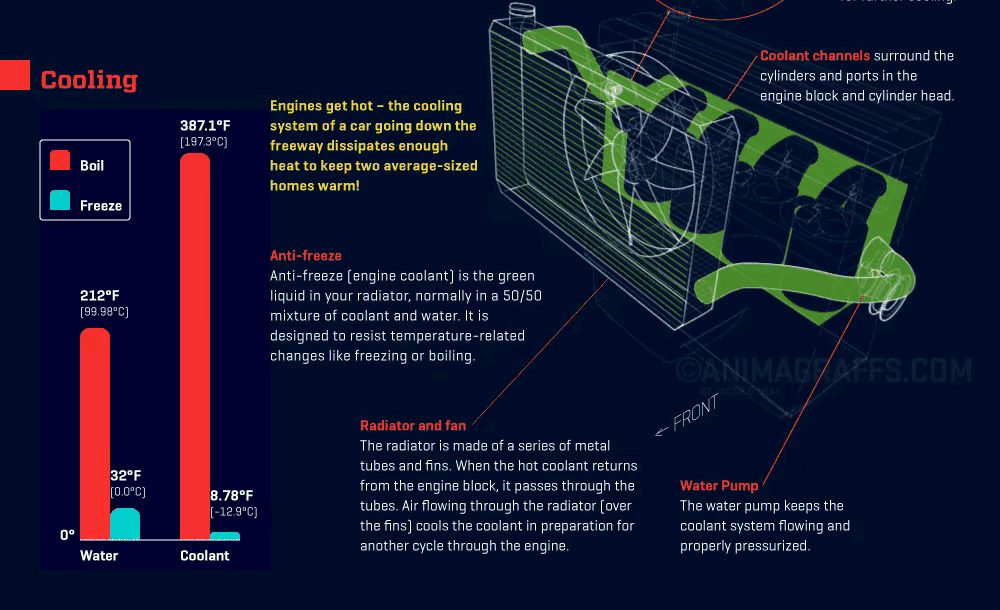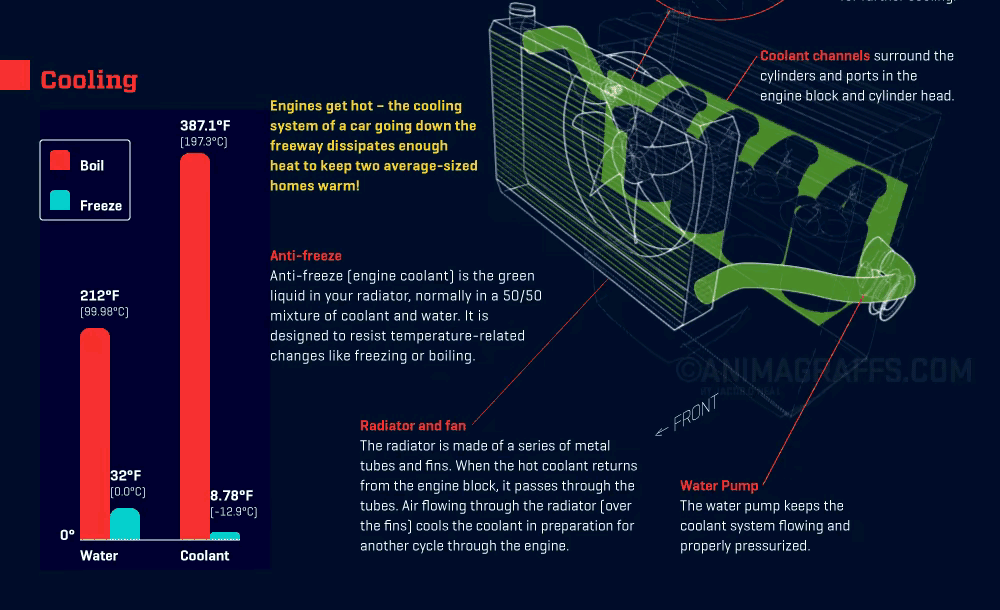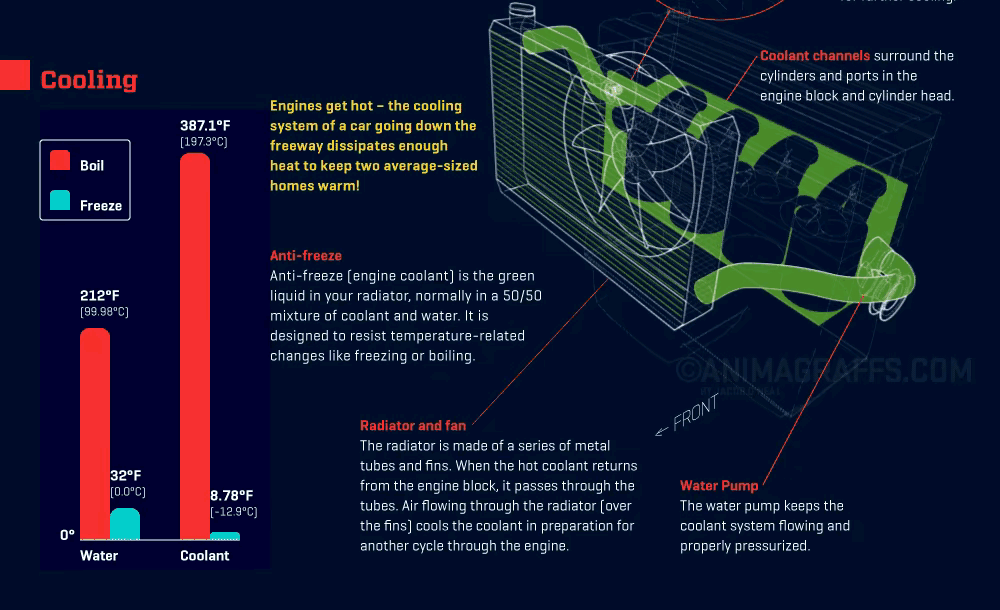
Coolant Flow and Heat Absorption: Coolant flows through the engine block and cylinder head, absorbing the generated heat and causing its temperature to rise.
-
Thermostat Regulation: Once the coolant reaches a certain temperature, the thermostat opens, allowing hot coolant to flow into the radiator to start the cooling process.

-
Heat Dissipation in the Radiator: The coolant enters the radiator’s core, which contains small tubes lined with fins. These fins maximize contact with outside airflow, allowing the coolant’s heat to dissipate quickly.
-
Coolant Recirculation: After cooling, the coolant exits the radiator and flows back to the engine, continuing the cycle and keeping the engine within the ideal temperature range.
Radiator Materials: Types and Selection
The material of a radiator significantly impacts its cooling performance and durability. Here are some common radiator materials and their characteristics:
-
- Features: Copper and brass radiators have excellent heat conduction, providing high cooling efficiency and durability, making them ideal for vehicles with high cooling needs (e.g., high-performance vehicles).
- Drawbacks: They are heavier, adding extra weight to the vehicle, and are relatively costly.

-
Aluminum Radiators
- Features: Aluminum radiators are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and have decent thermal conductivity, making them a practical choice for everyday vehicles.
- Drawbacks: Compared to copper/brass, aluminum radiators are slightly less effective in heat dissipation and slightly less durable.
-
Composite Radiators (Aluminum + Plastic)
- Features: These radiators combine aluminum cores with plastic tanks, balancing cooling performance and weight reduction, widely used in modern vehicles.
- Drawbacks: The plastic parts may age and degrade over time, reducing durability.
Material Selection Advice: Copper/brass radiators are preferred for high-performance demands, while aluminum or composite radiators are economical and suitable for standard driving needs.
Is Radiator Thickness Better if Thicker?
Radiator thickness isn’t necessarily better with increased thickness. Overly thick radiators can obstruct coolant flow, reducing cooling efficiency. Generally, the optimal radiator design includes an appropriate thickness, multiple rows, and efficient fin layout to ensure smooth coolant flow and effective cooling.
Key Components of the Cooling System: Selection and Evaluation
-
- Quality Characteristics: High-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and good flexibility. Premium rubber hoses often have reinforced material to withstand temperature changes and coolant corrosion, preventing cracking or leaks.
-
Radiator Cap
- Quality Characteristics: A good radiator cap provides strong sealing and the proper spring pressure, maintaining the system’s pressure to prevent premature coolant boiling. Check the sealing gasket and spring recoil, ensuring they’re in good condition, with no rust or wear.
-
Water Pump
- Quality Characteristics: A quality water pump has a sturdy build, stable bearings, and a precision-designed impeller, ensuring smooth, continuous coolant flow. It should be rust-free and show no signs of leakage, with a smooth-turning impeller.
-
Thermostats
Quality Characteristics: A reliable thermostat ensures proper engine temperature regulation by opening and closing at the specified temperature. It should feature a durable housing, corrosion-resistant components, and a precision-calibrated spring. A good thermostat prevents overheating and ensures optimal engine performance, showing no signs of sticking or irregular operation. -
Engine Oil Coolers & Lines
Quality Characteristics: High-quality engine oil coolers and lines are designed for efficient heat dissipation and long-term reliability. They should be made from corrosion-resistant materials, with reinforced lines that can handle high pressure without cracking or leaking. Look for leak-free connections and consistent cooling performance. -
Expansion & Overflow Tanks
Quality Characteristics: Premium expansion and overflow tanks are constructed with high-grade, heat-resistant plastics or metals. They should feature a secure cap, durable seams, and clear markings for monitoring coolant levels. A well-designed tank prevents coolant loss and ensures the system remains properly pressurized. -
Water Pumps
Quality Characteristics: As previously noted, quality water pumps ensure efficient coolant circulation with features like robust construction, precision impellers, and stable bearings. They must show no signs of leaks, rust, or impeller damage, ensuring long-lasting performance. -
Other Cooling Parts
Quality Characteristics: Supporting cooling components, such as gaskets, seals, and fittings, should be made of high-quality materials resistant to heat, pressure, and corrosion. These parts are essential for maintaining system integrity and preventing coolant loss or contamination. -
Fan & Shroud Assemblies
Quality Characteristics: Durable fan and shroud assemblies provide optimal airflow to the radiator, enhancing cooling efficiency. Look for shrouds with heat-resistant materials and fans with balanced blades to ensure smooth operation. The assembly should fit securely and operate without excess noise or vibration. -
Coolant Hoses
Quality Characteristics: Coolant hoses must be flexible yet robust, resisting temperature fluctuations and chemical degradation. Premium hoses often feature reinforced layers to prevent bulging or splitting under high pressure. Ensure tight, leak-free connections for reliable performance. -
Fan Motors
Quality Characteristics: A high-quality fan motor ensures consistent airflow to keep the radiator and engine at optimal temperatures. It should feature durable construction, smooth operation, and reliable connections. The motor should operate quietly without overheating or showing signs of wear. -
Temperature Sensors
Quality Characteristics: Accurate temperature sensors are critical for monitoring coolant and engine temperatures. A dependable sensor features precision engineering and corrosion-resistant contacts. It should provide real-time, consistent readings to ensure proper cooling system management.
Common Issues in the Cooling System and Solutions

-
Coolant Leaks: Often caused by damaged hoses, radiator cracks, or an aging water pump. Solution: Regularly check and replace any worn parts to prevent coolant shortages and overheating.
-
Overheating: Frequently due to thermostat, radiator clogs, or water pump issues. Solution: Inspect and replace faulty components, clean the radiator regularly, and ensure coolant flow is unobstructed.
-
Coolant Contamination: Mixing different coolants can cause chemical reactions, reducing system efficiency. Solution: Use only the recommended coolant type, avoiding the mixing of different coolants.
-
Fan Failure: A broken fan reduces cooling at low speeds. Solution: Regularly check fan operation and replace any faulty fan or switch components promptly.
Daily Maintenance Tips for the Cooling System
- Regular Coolant Replacement: Change the coolant every 30,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer to prevent corrosion buildup.
- Monitor Coolant Levels: Regularly check coolant levels and refill as necessary to keep the system running smoothly.
- Inspect for Wear: Routinely inspect hoses and radiator caps for wear, replacing aging components promptly.
- Avoid Coolant Mixing: Different coolants have unique formulations, and mixing them can cause system damage. Always use a single type when refilling or replacing coolant.
Conclusion
The importance of the cooling system in vehicle operation is undeniable. By choosing the right radiator material and performing regular maintenance, you can extend engine life and enhance vehicle efficiency. Whether through regular professional servicing or routine self-inspections, keeping an eye on the cooling system will ensure safer, more reliable driving experiences.