Ever noticed your car’s exhaust taking on a strange “new vibe”? Suddenly puffing black smoke, blue smoke, or white smoke—or even making odd noises? Don’t worry! These could be your exhaust system’s way of sending out a “help me!” signal. Today, let’s dive into the mysteries of the exhaust system with a lighthearted approach and turn you into a certified “exhaust detective”!

How the Exhaust System Works: It’s More Than Just “Blowing Smoke”
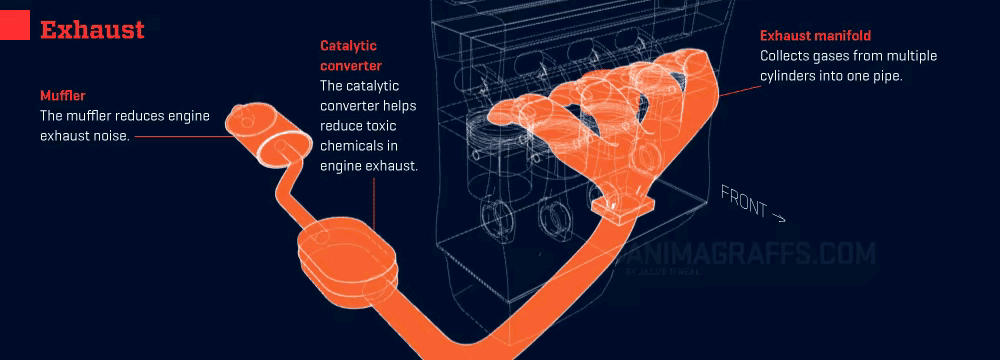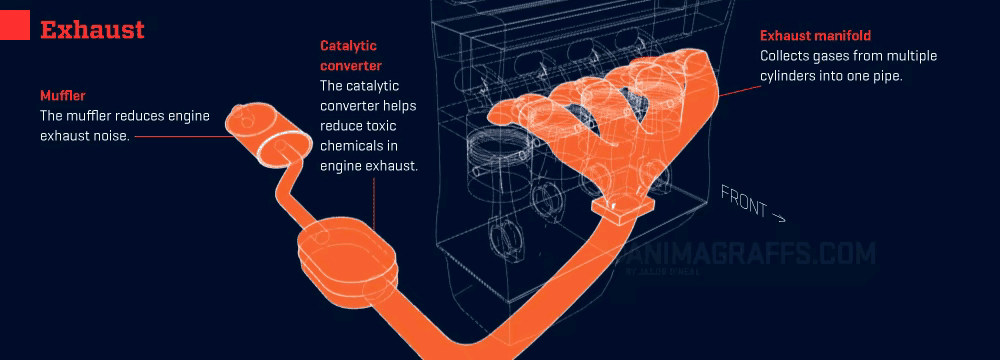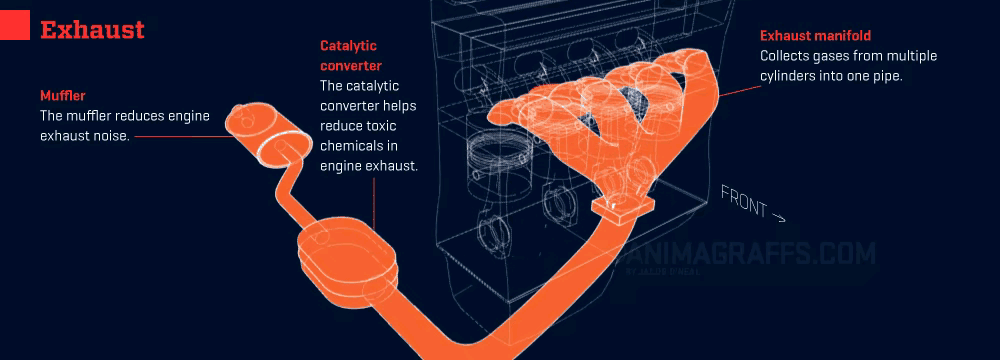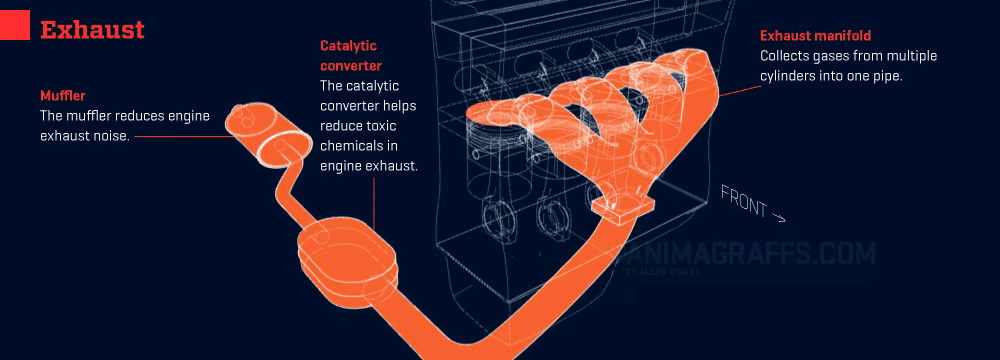
Your car’s exhaust system is like its “respiratory system,” tasked with expelling harmful gases while reducing noise and pollution. Keeping it smooth and clear ensures your engine runs efficiently and reliably.
Here’s the process in a nutshell:
- Exhaust Creation: High-temperature, high-pressure gases are produced as fuel burns in the engine’s cylinders.
- Exhaust Expulsion: Gases exit through the cylinder’s exhaust valves and enter the exhaust manifold.
-
Exhaust Treatment (Two Scenarios):
- With a Turbocharger: Exhaust gases spin the turbo’s blades, boosting air intake efficiency. Then, the gases flow into the catalytic converter.
- Without a Turbocharger: Exhaust gases move directly into the catalytic converter.
- Exhaust Purification: The catalytic converter—the system’s “cleaning guru”—transforms harmful gases (like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides) into less harmful ones (like carbon dioxide and water).
- Exhaust Release: The purified gases exit quietly through the muffler and tailpipe.
When functioning properly, the exhaust is clear and invisible. If smoke appears, the color can hint at underlying issues.
Meet the Key Players: The Main Components of the Exhaust System
The exhaust system operates as a team, with each part performing a critical role. Here are its “all-star members” and their “job descriptions”:
1. Exhaust System Kits
- Role: Channels exhaust gases while reducing noise.
- Location: Beneath the car, running from the engine to the tailpipe.
2. Catalytic Converter
- Role: Reduces emissions by converting harmful gases into less harmful ones.
- Location: Between the exhaust manifold and muffler.
3. Exhaust Gaskets
- Role: Seals connections to prevent gas leaks.
- Location: Between the engine, exhaust manifold, and catalytic converter.
4. Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve
- Role: Reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by reintroducing some exhaust gases into the combustion process.
- Location: Between the intake and exhaust systems.
5. Fuel Vapor Canister
- Role: Stores and releases fuel vapors to prevent pollution.
- Location: Near the fuel tank or exhaust pipe.
6. Solenoids
- Role: Controls the flow of exhaust gases or fuel vapors.
- Location: At critical points in the exhaust system.

How to Spot Quality Exhaust Parts
When choosing replacement parts for your exhaust system, quality is key. Here’s what to look for in each component:
Exhaust System Kits
- Material: Stainless steel or aluminum alloy for durability and corrosion resistance.
- Welding: Smooth, uniform welds at connection points to prevent leaks.
- Compatibility: Ensure proper length, diameter, and fit for your vehicle.
Catalytic Converters
- Material: High-quality ceramic or metal cores coated with platinum, palladium, and rhodium for effective gas conversion.
- Emissions Standards: Must meet local regulations, like Euro V or Euro VI.
- Design: A well-structured, damage-free core ensures optimal performance.
Exhaust Gaskets
- Material: Graphite or metal composite for high-temperature resistance.
- Sealing: Perfect sealing to prevent gas leaks. Check for flat, intact surfaces.
- Compatibility: Exact fit to your system’s joints.
EGR Valve
- Material: High-temperature and corrosion-resistant alloy.
- Functionality: Quick response to changes in exhaust flow; test manually or with diagnostics.
- Compatibility: Ensure proper fit between the intake and exhaust systems.
Fuel Vapor Canister
- Material: High-strength plastic or composite for durability.
- Functionality: Effective vapor absorption with intact seals.
- Compatibility: Properly matches your car’s mounting points.
Solenoids
- Material: Heat-resistant coils and corrosion-proof alloy bodies.
- Functionality: Smooth, rapid operation without sticking.
- Compatibility: Matches your car’s electrical and exhaust system.
What Does Your Exhaust Smoke Say?
Different smoke colors point to specific problems. Let’s break it down:
1. White Smoke
-
Causes:
- Normal: Water vapor in cold weather.
- Abnormal: Coolant leaking into the combustion chamber (blown gasket or cracked cylinder).
-
Diagnosis:
- Check for low coolant levels or a sweet smell in the exhaust.
- Look for a milky substance in the oil dipstick.
-
Fixes:
- Temporary: Use a head gasket sealer.
- Permanent: Replace the head gasket or repair the cylinder block.
2. Black Smoke
-
Causes:
- Rich fuel mixture due to a faulty fuel pressure regulator, leaking injectors, or clogged air filter.
-
Diagnosis:
- Check spark plugs for black carbon deposits.
- Use an OBD-II scanner to check for error codes (P0172, P0175).
-
Fixes:
- Clean or replace injectors.
- Replace faulty sensors or air filters.
3. Blue Smoke
-
Causes:
- Burning oil due to worn valve seals, piston rings, or a clogged PCV valve.
-
Diagnosis:
- Check oil levels.
- Perform a compression or leak-down test.
-
Fixes:
- Replace valve seals or the PCV valve.
- Repair piston rings if needed.
How to Keep Your Exhaust System Happy
Preventative maintenance is the best way to avoid exhaust issues. Here’s how:
- Schedule Regular Maintenance: Change oil, air filters, and spark plugs as recommended.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Prevent carbon buildup and blockages.
- Monitor Fluid Levels: Keep an eye on coolant and oil levels.
- Check for Blockages: Ensure the exhaust pipe and catalytic converter are clear.
- Address Warning Lights: Don’t ignore them—diagnose and fix issues promptly.
Exhaust Problem Cheat Sheet
| Smoke Color | Common Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| White Smoke | Coolant leak (blown gasket) | Replace the gasket or repair the cylinder block. |
| Black Smoke | Rich fuel mixture | Replace sensors, clean injectors, change filters. |
| Blue Smoke | Burning oil (worn seals/rings) | Replace valve seals or PCV valve, repair rings. |
Conclusion: Don’t Let Your Exhaust Lose Its Cool
Your car’s exhaust is like its health report—clear exhaust means all systems are go, while colored smoke signals that something’s off. By understanding these signs, you can confidently diagnose and resolve problems before they escalate. So the next time your car “blows smoke,” you’ll know exactly how to respond and get it back to running smoothly. 🚗💨